Startups from around the world have found crowdfunding to be an extremely viable alternative to traditional venture capital. To date, crowdfunding initiatives have raised $34 billion, which roughly added $65 billion to the global economy. There is a whole set of rules that a project needs to follow to get considered for VC funding. Plus, non-traditional and non-conventional projects often don’t get considered for VC funding.
However, the crowdfunding space has a lot of issues. Despite being a multi-billion dollar industry, specific issues have come to the surface, which shows that it is far from perfect. Many have looked at the blockchain technology as the ideal vehicle for improving this space. By providing greater transparency into individual campaigns and reducing the amount of trust required between backers and creators, crowdfunding can become a more robust means of fund distribution.
So, what are the use-cases of integrating the blockchain technology into crowdfunding? Let’s take a look.

#1 Decentralized
Crowdfunding Platforms
Traditional crowdfunding platforms like
Kickstarter and Indiegogo have raised billions of dollars in recent years, but
they often take a considerable cut of the profits for themselves. The fee
system of both these platforms are as follows:
- Kickstarter charges a 5% listing
fee and Stripe credit card processing charges of 3% + $0.20 per transaction.
- Indiegogo charges a 5% listing fee
on contributions and Stripe credit card processing charges of 3% + $0.30 per
transaction.
The problem with the listing fee system is
that it just incentivizes the platforms to take in as many projects as
possible, regardless of its credibility, to make a profit out of it.
So, how can decentralization help the crowdfunding space? Decentralization takes away the intermediaries and allows backers and creators to directly communicate with each other via smart contracts. Removing intermediaries also leads to less censorship over projects that may be considered by some to be controversial.

#2 Increasing
Opportunities for Wealth Creation
The wealth distribution on this planet is
extremely skewed. Here are some stats for you to ponder over:
- More than 3 billion people, that’s
nearly half of the world’s population, survive on less than $2.50 a day. - More than 1.3 billion live on less
than $1.25 per day. This condition is known as “extreme poverty.” - Sub-Saharan
Africa is the epicenter of extreme poverty. The number of “extremely poor”
living in this area went up to 9 million in 2015 alone. It is forecasted that 9
out of every 10 people living in extreme poverty will reside in Sub-Saharan
Africa by 2030. - Women in developing nations are 9%
less likely than their male counterparts to have a bank account. - Two billion people around the
world don’t even have a bank account. Of these, 438 million people are unbanked
in SE Asia alone, that’s 73% of the entire population living in the region
alone.
Cryptocurrencies will allow people to transact their money without having to go through a bank. There is no need for you to create a bank account and give them full power over your hard-earned money. For entrepreneurs from these demographics, who don’t have the means to reach out for traditional funding, blockchain-based crowdfunding can be a life-changer.

#3 Removing Middlemen
The crowdfunding platforms are currently
polluted with middlemen. Now only does the platform itself act as a middleman,
but the payment gateway act as another middleman. Then we have other middlemen
like Agency 2.0 and Crowdfund Mafia who help crowdfunding campaigners pick
which platform will be best for them. Obviously, all these intermediaries are
taking their own cut for the services provided.
A smart contract is a computer protocol
intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or
performance of a contract. It allows two parties to directly interact with each
other, without going through a third-party.
The term “smart contract” was coined by
cryptographer Nick Szabo back in the ’90s in his article “Smart
Contracts: Building Blocks for Digital Markets.” To understand
the philosophy behind how they work, let’s take Szabo’s vending machine
example.
Here is how you usually interact with a
vending machine:
- You choose the item that you want.
- You put in some cash inside the
machine. - The machine gives you the item.
Pretty straightforward right? However, there
are two things that you need to note during this entire interaction:
- Each step can’t be executed until
the preceding step has been fulfilled. Eg. You can’t put in the money until you
select what you want. Also, the machine can’t give you an item until you put in
the money. - During this entire interaction,
you and the machine are directly interacting with each other. There is no
third-party, like a shopkeeper, between the two of you.
This right here are the core principles behind
smart contracts:
- The two parties bound in a smart
contract can directly interact with each other. - Each step in a smart contract can
only be fulfilled after the execution of the preceding step.
The smart contract will allow creators to connect with the backers directly. The smart contract’s predefined conditions can dictate how the funds will flow. This is extremely important for the next part.

#4 Ensuring Backer
Protection
In Pledgecamp – a blockchain-based
crowdfunding platform, the backers will enter into a smart contract with the
creator. The backer will then contribute their funds, a percentage of which is
held in escrow within the contract. These funds will be released to the creator
only when they meet certain milestones. These milestones are pre-defined before
the funds are raised so that the expectations between creators and backers are
clear from the beginning.
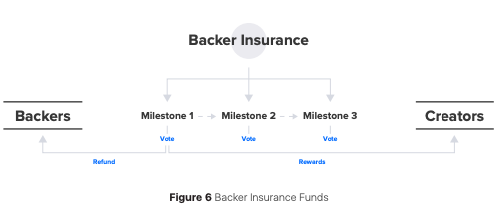
Backers will then verify the milestones through a democratic vote. If the milestones are not met, then the backer insurance funds are refunded to the backers. Otherwise, it is credited to the creator.

#5 Lowering Listing Fees
Also, traditional crowdfunding platforms take enormous listing fees from creators for hosting their crowdfunding campaigns. Many decentralized crowdfunding platforms will allow the creators to forego the listing fees altogether. All they need to do is to allow their backers to lock up a generous amount of their investment in the escrow contract. The idea is that if you are confident about your project, then you can host it for free!

#6 Incentivizing Platform
Community
A decentralized crowdfunding platform will
also build an environment where its community can be rewarded for performing
tasks, aka “bounties.” These bounties could be:
- Content Creation: Create YouTube videos, blog
posts, infographic creation, logo/branding design, etc.
- Social Media Promotion: Provide exposure for
the creator’s campaigns by sharing links, retweets, posting to Facebook,
Instagram, etc.
- Survey Creation: Fill out surveys to help
collect market research data
- Localization/Translation: Translate marketing
material, product descriptions, or product manuals into additional languages
for greater reach.
These bounties can help create a “gig
economy,” which can be automated, scaled, and tracked all over the world.
Economically monetizing these activities will incentivize users to use their
passion and skills to grow the creator’s project dynamically.
The members of the community in certain platforms can also stake the native tokens to become “Moderators” within the system. These moderators help in keeping the network healthy and the platform as spam-free as possible.

#7 ICO/IEO/STO
Finally, we have the ICOs/IEOs/STOs (initial
coin offerings/ initial exchange offerings/security token offerings). These are
public crowdsales where cryptocurrency projects can raise funds. The ICOs have
been truly revolutionary and have managed to accomplish many amazing tasks:
- They have provided the most
straightforward path by which DAPP developers can get the required funding for
their projects.
- Anyone can become invested in a
project they are interested in by purchasing the tokens of that particular DAPP
and become a part of the project themselves.
The truly remarkable fact about these
crowdsales is that projects can raise millions of dollars with just a
whitepaper. They are not required to show a rudimentary version of their
product to secure the funding. The first-ever recognized ICO was held by
Mastercoin in July 2013. Mastercoin was able to raise about a million dollars.
The ICO landscape has been riddled with some
high-profile scams, which gave rise to safer alternatives such as STOs and
IEOs.
Conclusion
The blockchain technology is truly
game-changing. As we can see, the crowdfunding space can integrate it to raise
their game to the next level.
The post Possible Use-Cases for Blockchain-based Crowdfunding appeared first on Cryptoverze.